

Custom Search
|
|

|
||
 TM 5-683/NAVFAC MO-116/AFJMAN 32-1083
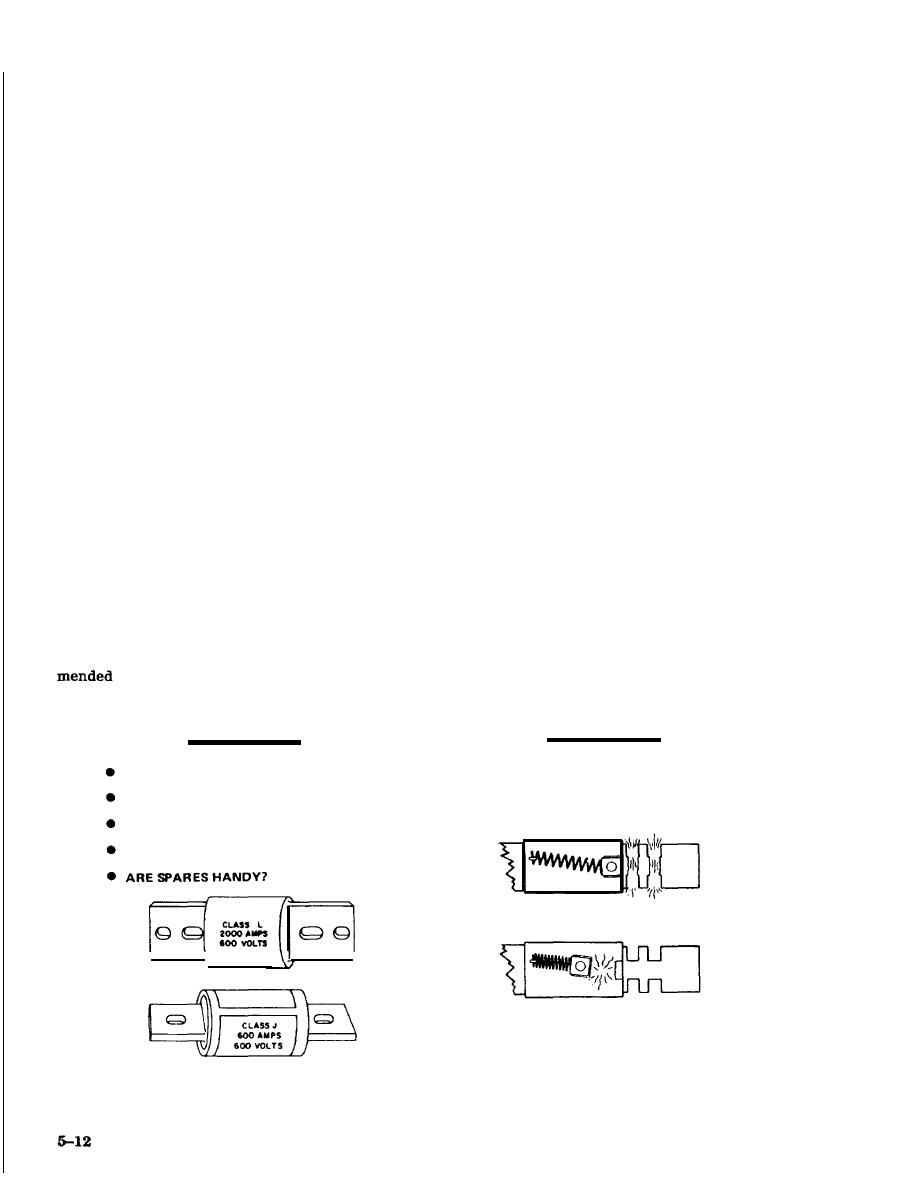
placed. Replace fuses showing signs of deterioration
magnetic fields. The test setup must be conducted
in such a way that magnetic fields created by the
such as discolored or damaged casings or pitted
test equipment, steel enclosures, or the conductors
contact surfaces. There are many types of fuses (fig
from the test equipment to the circuit breaker do
5-13) with various characteristics, some of which
not affect the test results.
are physically interchangeable. Make certain that
d. Fuses. Fuses are among the oldest types of
fuses are of the proper type and rating. Never re-
overcurrent protectors. They are simple, rugged and
place one type of fuse arbitrarily with another type
inexpensive. They sense overcurrent conditions
fuse of the same physical size simply because it fits
through the development of heat in the conducting
the fuse holder. A continuity check should also be
elements and accomplish their operation by de-
performed on replacement fuses to ensure their in-
struction of these elements. They offer both long-
tegrity. Fuses should have correct current and volt-
time and short-time short circuit protection and are
age ratings, proper time-delay or current-limiting
used widely in the protection of small motors. Main-
characteristics and an adequate interrupting rating
tenance of fuses should not be performed until all
to protect the circuit and its components Current
power sources are disconnected (fig 5-12). At that
ratings of fuses protecting transformers or motors
time, check the continuity of all fuses with an ohm-
should be selected at or near the fill load current.
meter. A reading greater than zero ohms indicates
Voltage ratings of fuses should equal or exceed their
that the fuse is blown and must be replaced. Inspect
circuit voltage. Interrupting ratings of fuses should
fuse terminals and fuse holder clips. Check that the
equal or exceed the available fault current at the
portions of the fuse making contact in the clip are
fuse holder. UL listed fuses without marked inter-
clean and bright; poor contact can cause overheat-
rupting ratings are satisfactory only on circuits
ing which results in a discoloration of the contact
where fault currents do not exceed 10,000 amperes.
surfaces. If this occurs, then the oxidized surfaces
Non-current-limiting fuses should not be used to
should be cleaned and polished. Silver-plated sur-
replace current-limiting fuses since fuse holders for
faces should not be cleaned with an abrasive mate-
UL listed current-limiting fuses are designed to re-
rial. Wiping contacts with a noncorrosive cleaning
agent is recommended. Tighten all fuse holder con-
ject fuses which are not current limiting. Fuse hold-
nections. Fuse clips should exert sufficient pressure
ers and rejection clips should never be altered or
forced to accept fuses which do not readily fit. An
to maintain good contact, which is essential for
proper fuse performance. Clips which make poor
adequate supply of spare fuses, especially those
which are uncommon, will minimize improper re-
contact should be replaced. Clip clamps are recom-
when unsatisfactory clips cannot be re-
placement.
CORRECTIVE
PREVENTIVE
MAINTENANCE
MAINTENANCE
q TEST FOR CONTINUITY, SINGLE PHASING
IS FUSE TIGHT IN CIRCUIT?
q WHAT OPENED FUSE?
ARE FUSE AND HOLDERS CLEAN AND DRY?
-- SHORT?
OVERHEATING?
ARE RIGHT TYPE AND SIZE IN CIRCUIT?
--
OVERLOAD?
--
HIGH TEMPERATURE DERATING?
q REPLACE WITH RIGHT TYPE AND SIZE.
Figure 5-12. Fuse maintenance practices.
|
 
|
|
 |
||