

Custom Search
|
|

|
||
 MIL-HDBK-419A
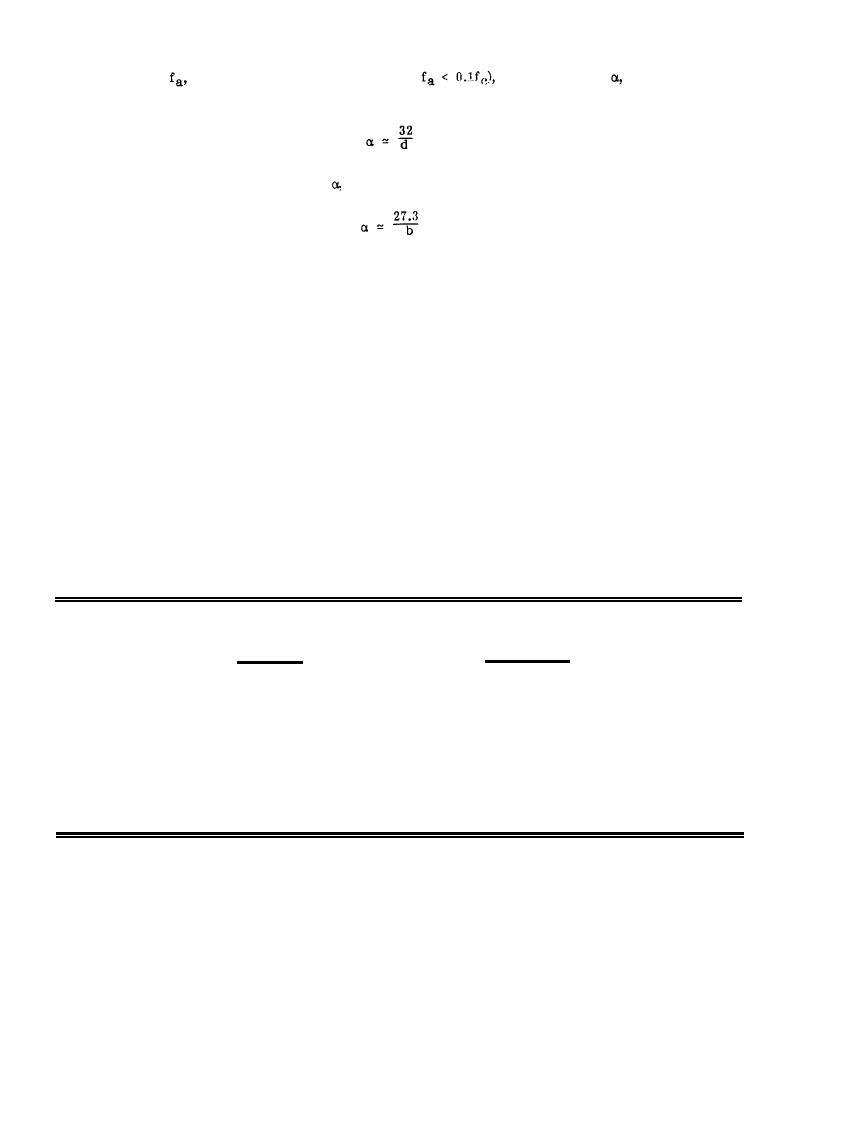
the attenuation,
in dB per inch for
At any frequency,
considerably less than cutoff (i.e.,
cylindrical waveguides is approximated by the relation
(8-27)
For rectangular waveguides, the attenuation,
in dB per inch is
(8-28)
The equations given above are valid for air-filled waveguides with length-to-width or length-to-diameter ratios
of 3 or more.
In many cases, shielding screens introduce excessive air resistance (See Vol II) and may provide inadequate
shielding effectiveness. In such cases, openings may be covered with specially designed ventilation panels (such
as honeycomb) with openings that operate on the waveguide-below-cutoff principle.
The shielding
effectiveness of honeycomb panels is a function of the size and length of the waveguide and the number of
waveguides in the panel. Table 8-16 indicates the shielding effectiveness of a honeycomb panel constructed of
steel with 1/8-inch hexagonal openings 1/2-inch long.
Table 8-16
Shielding Effectiveness of Hexagonal Honeycomb Made of Steel
with 1/8-inch Openings 1/2-Inch Long (8-10)
Shielding
Effectiveness
Frequency
(dB)
(MHz)
0.1
45
50.0
51
100.0
57
500.0
56
2,200.0
47
Honeycomb-type ventilation panels in place of screening:
allow higher attenuation that can be obtained with mesh screening over a specified frequency range,
a.
8-51
|
 |
|
 |
||