

Custom Search
|
|

|
||
 MIL-HDBK-1027/3B
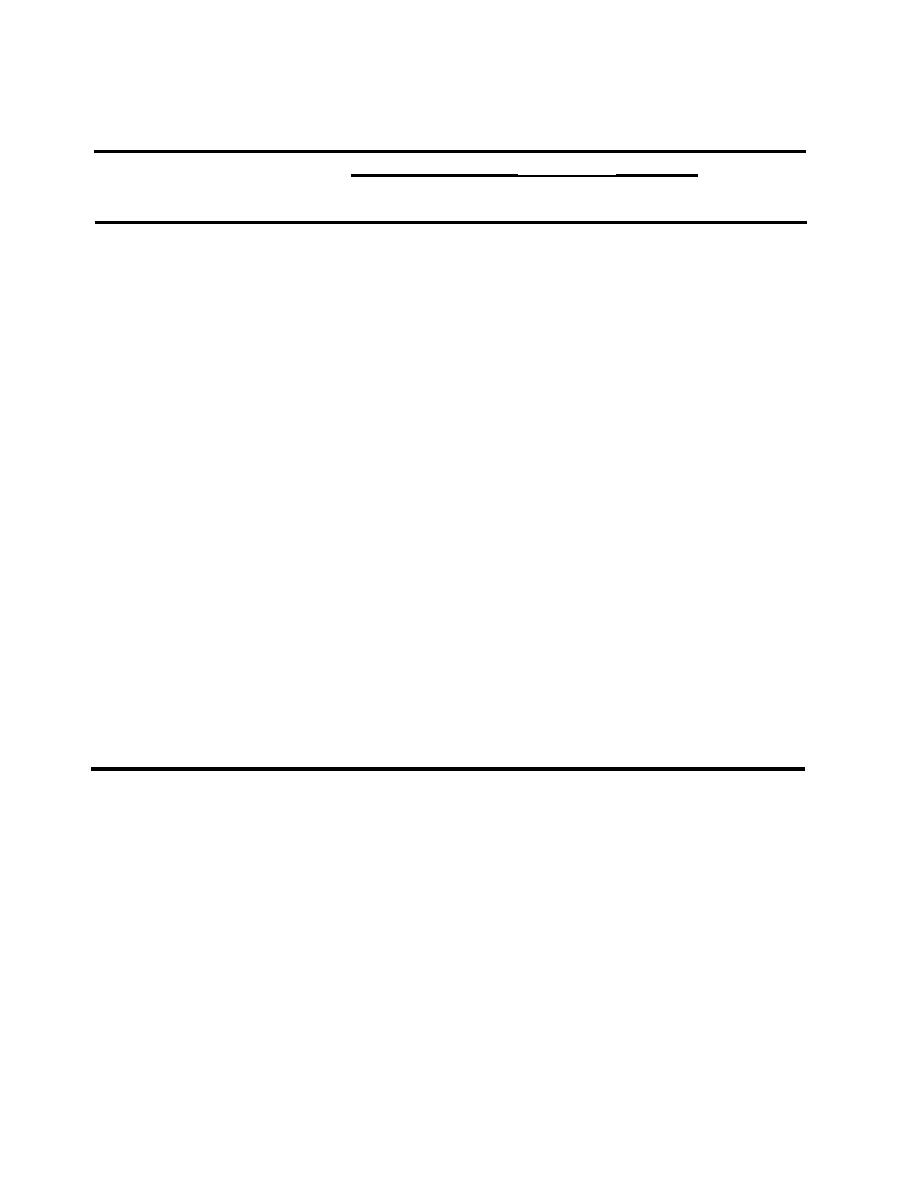
Table 3
Maximum Allowable Exposure Limits for Intermittent Atmospheric Lead
MAXIMUM HOURS OF ALLOWABLE EXPOSURE
AIRBORNE
LEAD CONCENTRATION
FIRING LESS THAN 30
FIRING 30 OR MORE
(micrograms/cu m)
DAYS/YEAR
DAYS/YEAR
Hrs/Week Hrs/Day
Hrs/Day
Hrs/Week
- 0.03
0
8
40
8
40
0.03 - 0.05
8
8
24
32
0.05 - 0.10
6
12
6
18
0.10 - 0.15
4
4
8
12
0.15 - 0.20
3
6
3
9
0.20 - 0.25
2 1/2
2 1/2
4 1/2
7 1/2
0.25 - 0.30
2
4
2
6
- 0.4
0.3
1 1/2
3
1 1/2
4 1/2
- 0.5
1
0.4
2 1/2
1
3
- 0.7
0.5
1/2
1/2
1 1/2
1 1/2
- 1.0
0.7
1/2
1/2
1
1
- 2.0
1.0
1/4
1/4
1/2
1/4
- 4.0
2.0
1/4
1/4
1/4
1/4
4.00
0
0
0
0
Wall treatment should be installed in not larger than four foot wide
panels to facilitate replacement after damage. Install. acoustic wall
treatment on furring strips spaced away from the wall. Ventilation duct
openings should have noise traps to reduce noise transmission to outside or
other occupied building areas. The floor area behind the firing line may be
covered with acoustic material that can withstand the chosen lead removal
process. While carpet is not recommended, it need not be removed from
existing facilities. Airborne noise can be reduced by sealing off air leaks.
Doors should be solid core, weather stripped. Provide double doors (air lock
arrangement) when connecting directly with another pert of a larger building.
Double glazing of windows into control rooms will reduce transmission.
15
|
 |
|
 |
||