

Custom Search
|
|

|
||
 MIL-HDBK-232A
tunnel has a cutoff frequency of 75 MHz. Each conductor entering and exiting
the facility must be equipped with protection devices to shunt the high
lightning, or HEMP. Metal oxide varisters (MOVs), gas-filled spark gaps, and
carbon blocks are used in various combinations to achieve protection.
Low-voltage protection devices are also installed on the facility entrance
plate.
5.4.3.2 Distribution frames (DFs). DFs are used to provide a means to
configure internal equipment for various applications. Typically, DFs
connect egressing lines to modems, modems to COMSEC devices, and COMSEC
devices to terminal equipment. A DF must be sized to accommodate every
signal line and its return and to provide a point to ground the shields to
the equipotential ground plane. The shield grounding scheme must allow for
the shortest possible exposure of unshielded pairs. This scheme must also
provide a minimum impedance path to the equipotential ground plane. Where
possible, the DF should also incorporate shielded pairs to effect
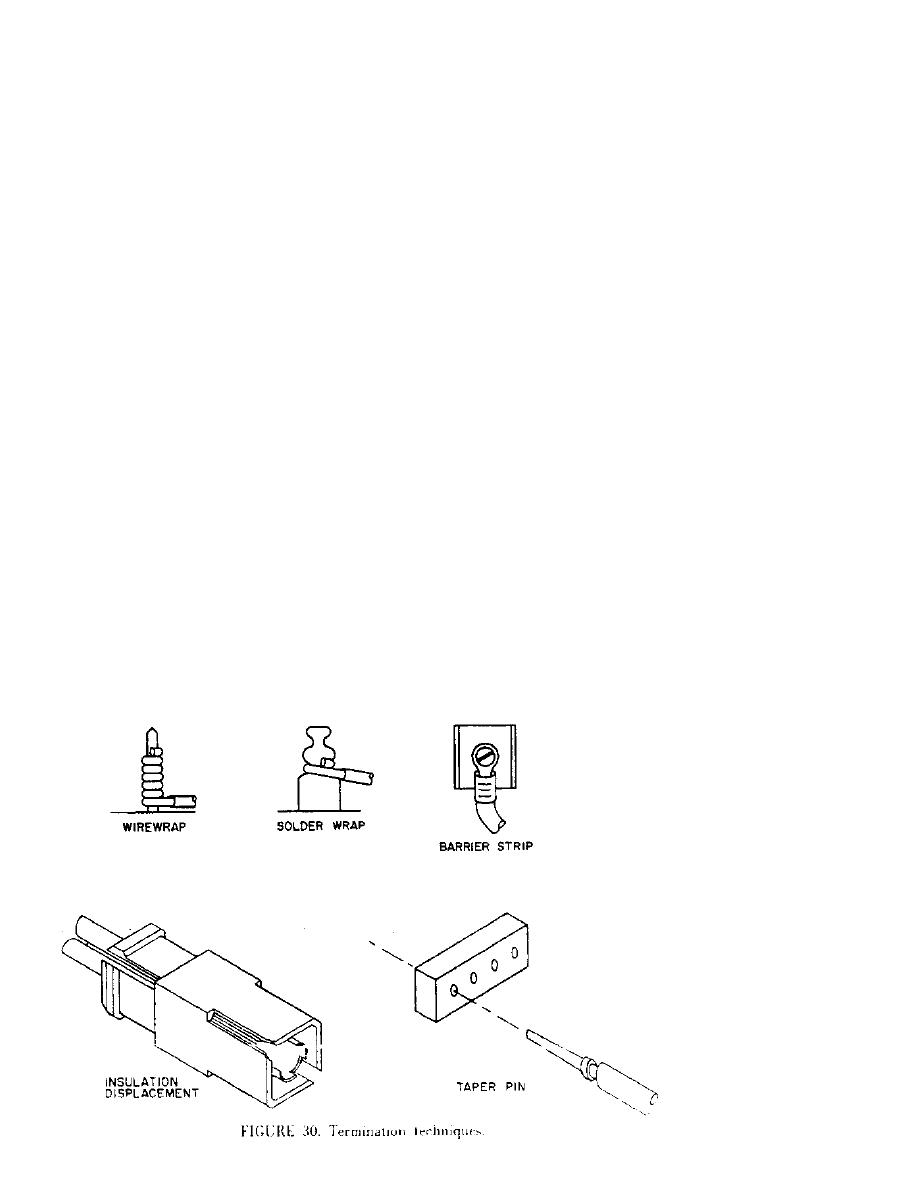
crossconnects. DF technology includes taper pins, connectorized backplanes,
solder lugs, insulation displacement techniques, and wire wraps (see figure
30). Taper pins are simple to terminate, but tend to corrode rapidly,
resulting in poor bonding. Connectorized backplanes do not provide
sufficient backshell contact to assure shield integrity unless the shields
are terminated separately in some manner other than the backshell.
Insulation displacement techniques rely on spring tension to grasp conductors
but lack a large surface area contact. Solder lugs are prone to cold solder
joints. Wire-wrap methods are the most reliable termination techniques due
to high mechanical reliability and large surface area contact. DFs should be
contained in metallic cabinets in RED areas. Separate DFs are needed for
each application (i.e., a RED digital DF for the RED equipment to RED patch
bays to COMSEC; a BLACK digital DF for COMSEC to BLACK patch bays to modems,
etc.). If DF's are housed in metallic cabinets, the cabinets should be sized
large enough for maintenance access.
|
 |
|
 |
||