

Custom Search
|
|

|
||
 CAMEL OR CAVE CRICKETS
Ceuthophilus
CRICKETS
Family Gryllidae
Crickets are well-known relatives of cockroaches
and katydids. Like katydids, male crickets "sing" in
the summer by moving hard parts of their wings
together; the males are calling females for mating.
They develop with gradual metamorphosis; during
some periods, adults and nymphs share the same
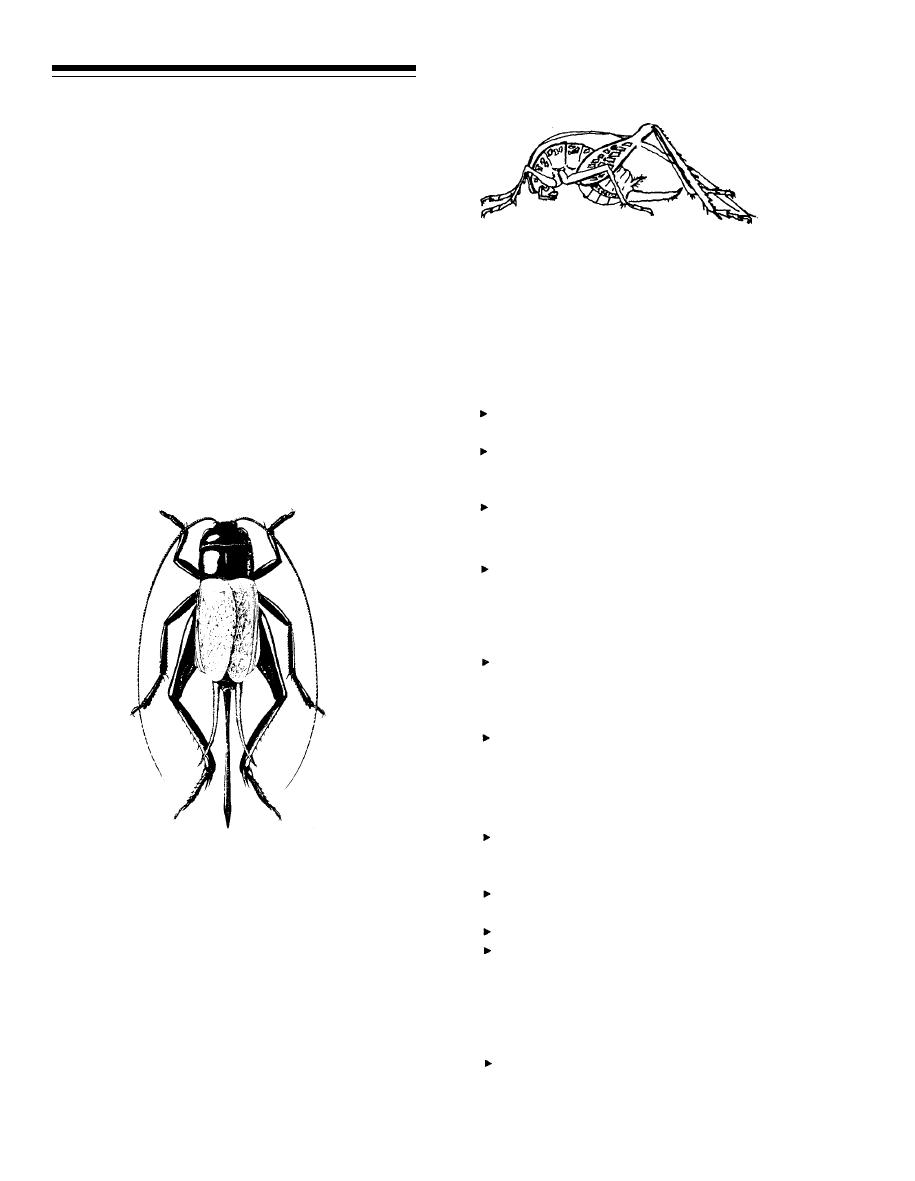
This humpbacked insect is more closely related to
harborage and food with grasshoppers.
katydids than to crickets. It is mottled brown and
wingless with very long legs and antennae. Cave
FIELD CRICKETS
crickets are often compared to spiders, but the
resemblance is only superficial. Cave crickets prefer
The most commonly-seen crickets in the United
dark damp or cool places like basements, crawl
States are field crickets; adults are very dark and about
spaces, and garages. They seldom cause damage.
one inch long. Eggs are laid toward the end of
summer in moist soil of roadside ditches, meadows
Inspection
and fields, along fences; and in dry weather, they are
Locate the egg laying sites where
laid in soil cracks, where adult crickets find some
populations build up, if possible.
moisture for egg laying as well as for themselves.
Look near patches of weeds, soil
Eggs are injected into soil by the female using a long,
cracks, at the base of plants, or in
straight appendage called an ovipositor. The eggs
grass.
overwinter and hatch in spring.
Inspect basements, closets, pantries.
Habitat Alteration
Caulk, tighten, and weatherstrip
basement and ground floor doors and
windows to keep crickets out of houses.
Thin plantings next to building
foundations.
Keep grass short during cricket activity
to discourage the insects and reduce
cover in case pesticide sprays are
needed.
Ventilate and remove materials that
provide hiding places for cave crickets
in crawl spaces and garages.
Pesticide Application
Direct pesticide spray applications in
Crickets feed on plants, and mature in July and
cracks near the foundation and around
August. When weeds begin to harden and die and rain
door stoops and patios.
is sparse, crickets often leave their ditches and fields;
Apply a residual barrier around the
they move out in massive invasions. This is the time
building if populations are very high.
they come into homes and buildings. Entry into
Use granular baits when needed.
structures is most always under doors and through
Where very high build-up is detected in
opened windows.
breeding areas, particularly in a series
Field cricket populations are cyclical. Some years
of cricket invasion years, spray the
great numbers find their way across parking lots and
weeds and grass in midsummer with
into malls and office buildings. Many years of low
pesticides labeled for cricket control on
cricket populations may follow. Other crickets like the
plants.
house cricket, and the very small dark brown
Advise clients to swat field and cave
Nemobius, also have cycles of build up and movement
crickets indoors or spray them with a
general use contact aerosol.
into structures.
Module Two, Chapter 5, Pg 2
|
 |
|
 |
||